Testing REST API with Serenity and Rest-assured
Rest-assured is a Java framework for testing and validating REST APIs.
Serenity is an automated BDD(Behaviour driven development) acceptance testing framework. Rest-assured combined with Serenity in connection provides a tool for easy creating of BDD api tests and generates neat and good looking reports.
Test project
In the scope of article, postcodes.io api will be tested.
Postcodes is a free, Open Source api for Postcode and Geolocation for the UK.
Project structure
It uses standard maven project structure.
postcodes-api-tests
src
pom.xml
test
java
pl.jlabs
cukes
RunCukes.java
stepdefs
BaseTest.java
NearestPostcodesSteps.java
RandomPostcodeSteps.java
ValidatePostcodeSteps.java
PostcodesEndpoints.java
resources
features
NearestPostcode.feature
RandomPostcode.feature
ValidatePostcode.featurepom.xml
<!--?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?-->
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemalocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelversion>4.0.0</modelversion>
<groupid>pl.jlabs</groupid>
<artifactid>restassured-serenity</artifactid>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<restassured.version>3.3.0</restassured.version>
<hamcrest.version>1.3</hamcrest.version>
<json.version>20180813</json.version>
<serenity.version>2.0.81</serenity.version>
<serenity.maven.version>2.0.81</serenity.maven.version>
<serenity.cucumber.version>1.0.21</serenity.cucumber.version>
<cucumber.version>4.2.0</cucumber.version>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<parallel.tests>4</parallel.tests>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-core</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupid>io.cucumber</groupid>
<artifactid>cucumber-core</artifactid>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>io.cucumber</groupid>
<artifactid>cucumber-java</artifactid>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>io.cucumber</groupid>
<artifactid>cucumber-junit</artifactid>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-junit</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-rest-assured</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-cucumber4</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>junit</groupid>
<artifactid>junit</artifactid>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.assertj</groupid>
<artifactid>assertj-core</artifactid>
<version>3.6.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.hamcrest</groupid>
<artifactid>hamcrest-all</artifactid>
<version>1.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupid>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupid>
<artifactid>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactid>
<version>2.22.1</version>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactid>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactid>
<version>2.22.1</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*Cukes.java</include>
</includes>
<parallel>classes</parallel>
<threadcount>${parallel.tests}</threadcount>
<forkcount>${parallel.tests}</forkcount>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupid>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupid>
<artifactid>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactid>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.maven.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Serenity is compatible with Cucumber in version 2.x and 4.x. To use Cucumber in 4.x version, cucumber-core needs to be excluded from serenity-core.
The Maven failsafe plugin and serenity-maven-plugin needs to be configured to generate a test report.
PostcodesEndpoint.java
Enum with endpoints urls.
package pl.jlabs;
public enum PostcodesEndpoints {
NEAREST("postcodes?lon={lon}&lat={lat}"),
RANDOM("/random/postcodes"),
VALIDATE("postcodes/{postcode}/validate");
private final String url;
PostcodesEndpoints(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
}RunCukes.java
Cucumber tests runner
package pl.jlabs.cukes;
import cucumber.api.CucumberOptions;
import net.serenitybdd.cucumber.CucumberWithSerenity;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(CucumberWithSerenity.class)
@CucumberOptions(
plugin = {"pretty"},
features = "classpath:features",
glue = {"pl.jlabs.stepdefs"}
)
public class RunCukes {}NearestPostcodesSteps.java
package pl.jlabs.stepdefs;
import PostcodesEndpoints;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Given;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Then;
import cucumber.api.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import static net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest.restAssuredThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
public class NearestPostcodesSteps extends BaseTest {
private static final Map<string,object> VALID_GPS_DATA = Stream.of(
new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>("lon", "0.629834723775309"),
new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>("lat", "51.7923246977375"),
new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>("postCodes", new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("CM8 1EF", "CM8 1EU", "CM8 1PH", "CM8 1PQ"))))
.collect(Collectors.toMap(AbstractMap.SimpleEntry::getKey, AbstractMap.SimpleEntry::getValue));
private static final List<string> COORDINATES_OUTSIDE_UK = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("50.049683", "19.944544"));
@Given("the request with valid coordinates to the Nearest Postcodes endpoint")
public void theRequestWithAValidCoordinatesToTheNearestPostcodesEndpoint() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lon"))
.pathParam("lat", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lat"));
}
@Given("the request with invalid longitude")
public void theRequestWithInvalidLongitude() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(3))
.pathParam("lat", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lat"));
}
@Given("the request with valid coordinates outside UK")
public void theRequestWithAValidCoordinatesOutsideUK() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", COORDINATES_OUTSIDE_UK.get(0))
.pathParam("lat", COORDINATES_OUTSIDE_UK.get(1));
}
@Given("the request with invalid latitude")
public void theRequestWithInvalidLatitude() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lon"))
.pathParam("lat", RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(3));
}
@When("the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint")
public void theRequestIsMadeWithGetMethod() {
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.NEAREST.getUrl());
}
@Then("the response with a correct list of postcodes is returned")
public void theResponseWithACorrectListOfPostcodesIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", hasSize(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).size()))
.body("result[0].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(0)))
.body("result[1].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(1)))
.body("result[2].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(2)))
.body("result[3].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(3))));
}
@Then("an empty result list is returned")
public void anEmptyResultListIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", is(nullValue())));
}
@Then("the invalid longitude latitude submitted error is returned")
public void theInvalidLongitudeLatitudeSubmittedErrorIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST)
.body("status", equalTo(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST))
.body("error", equalTo("Invalid longitude/latitude submitted")));
}
}To use Rest-assured, Serenity provides class SerenityRest.
For BDD use, it’s called twice. In Given step:
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lon"))
.pathParam("lat", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lat"));and in When step, where the call is made to API:
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.NEAREST.getUrl());To analyze the response SerenityRest method the restAssuredThat method is called.
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST)
.body("status", equalTo(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST))
.body("error", equalTo("Invalid longitude/latitude submitted")));Another construction of assertion is also possible with use of a SerenityRest object:
SerenityRest.then()
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", is(notNullValue()));RandomPostcodeSteps.java
package pl.jlabs.stepdefs;
import PostcodesEndpoints;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Given;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Then;
import cucumber.api.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import static net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest.restAssuredThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.notNullValue;
public class RandomPostcodeSteps extends BaseTest {
@Given("a request to the random postcodes endpoint")
public void aRequestToTheRandomPostcodesEndpoint() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI);
}
@When("the request is made with the get method to random postcode")
public void theRequestIsMadeWithTheGetMethodToRandomPostcode() {
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.RANDOM.getUrl());
}
@Then("the randomly generated postcode is returned")
public void theRandomlyGeneratedPostcodeIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", is(notNullValue())));
}
}ValidatePostcodeSteps.java
package pl.jlabs.stepdefs;
import PostcodesEndpoints;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Given;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Then;
import cucumber.api.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import static net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest.restAssuredThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
public class ValidatePostcodeSteps extends BaseTest {
@Given("the request with a valid postcode")
public void theRequestWithAValid() {
validatePostCodeRequest(VALID_POST_CODES_LIST.get(0));
}
@Given("the request with an invalid postcode")
public void theRequestWithAnInvalidPostcode() {
validatePostCodeRequest(getRandomInvalidPostCode());
}
@Given("the request without postcode")
public void theRequestWithoutPostcode() {
validatePostCodeRequest("");
}
@When("the request is made with the get method to validate postcode")
public void theRequestIsMadeWithTheGetMethodToValidatePostcode() {
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.VALIDATE.getUrl());
}
@Then("the response with a result equal to {string} is returned")
public void theResponseWithAResultEqualToIsReturned(String expectedResult) {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", equalTo(Boolean.valueOf(expectedResult))));
}
@Then("the not found status code with an Invalid postcode error is returned")
public void theNotFoundStatusCodeWithInvalidPostcodeErrorIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_FOUND)
.body("error", equalTo("Invalid postcode")));
}
private void validatePostCodeRequest(String postCode) {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("postcode", postCode);
}
}NearestPostcode.feature
A Feature file with scenarios for nearest postcode endpoint
Feature: Nearest postcode
Scenario: A correct list of postcodes is returned for valid coordinates
Given the request with valid coordinates to the Nearest Postcodes endpoint
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then the response with a correct list of postcodes is returned
Scenario: An empty results list is returned for a valid coordinates outside UK
Given the request with valid coordinates outside UK
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then an empty result list is returned
Scenario: An invalid longitude/latitude submitted error is returned for a request with invalid longitude
Given the request with invalid longitude
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then the invalid longitude latitude submitted error is returned
Scenario: An invalid longitude/latitude submitted error is returned for a request with invalid latitude
Given the request with invalid latitude
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then the invalid longitude latitude submitted error is returnedRandomPostcode.feature
A feature file with scenarios for generating random postcode endpoint
Feature: Random postcode
Scenario: A random postcode is generated
Given a request to the random postcodes endpoint
When the request is made with the get method to random postcode
Then the randomly generated postcode is returned
ValidatePostcode.feature
A feature file with scenarios for validating postcode endpoint
Feature: Validate postcode
Scenario: True is returned for a request with a valid postcode
Given the request with a valid postcode
When the request is made with the get method to validate postcode
Then the response with a result equal to "true" is returned
Scenario: False is returned for a request with an invalid postcode
Given the request with an invalid postcode
When the request is made with the get method to validate postcode
Then the response with a result equal to "false" is returned
Scenario: Not found with an invalid postcode error is returned for a request without postcode
Given the request without postcode
When the request is made with get method to validate postcode
Then the not found status code with an Invalid postcode error is returned
Test execution
To execute tests use the maven command:
mvn clean verify
Test report
After test execution in directory target/site/serenity a report will be generated. To display the report open index.html
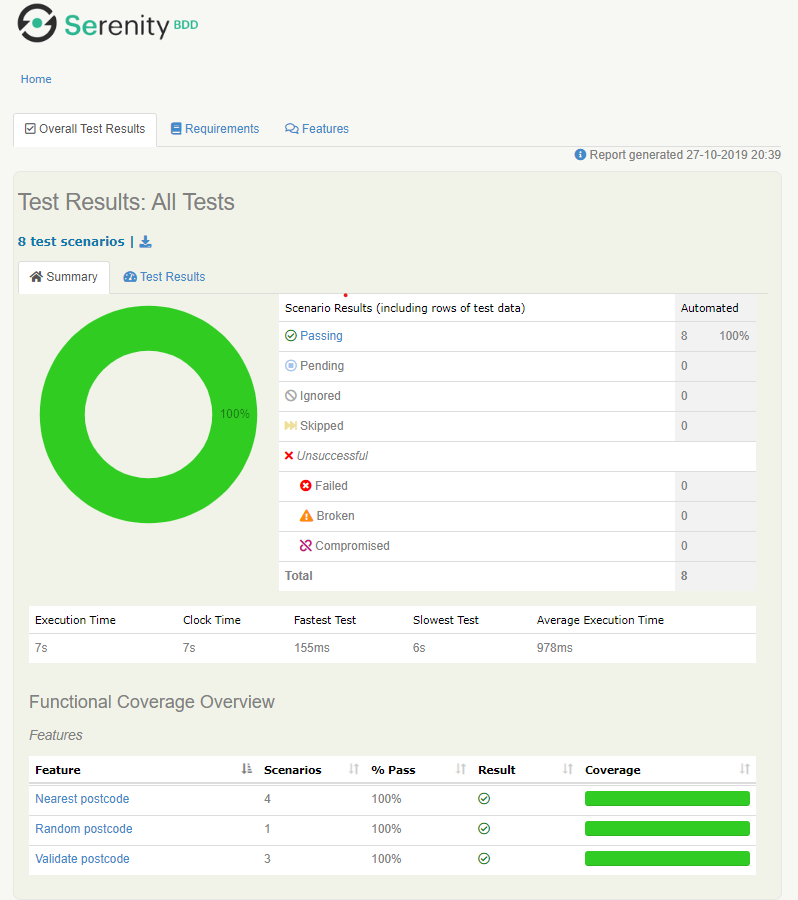
The report is well formatted and contains consolidated results.
In the Test Results tab detailed scenario reports are available for each scenario. A report for the scenario True is returned for a request with a valid postcode:
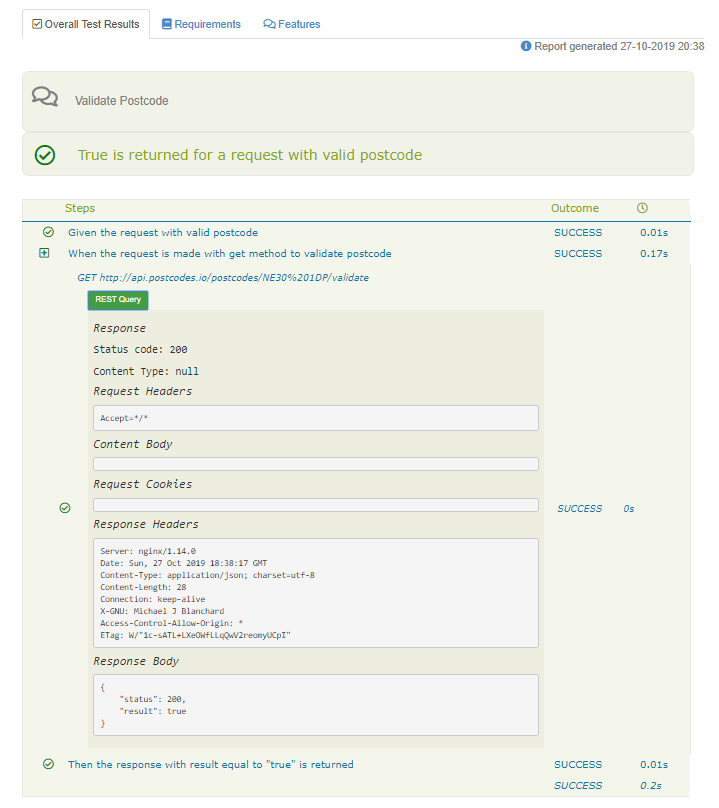
With the use of REST Query button it’s possible to display query details. Visible details:
- Path
- Status code
- Request Headers
- Request Body
- Request Cookies
- Response Headers
- Response Body
Summary
Serenity combined with Rest-assured makes a perfect set for developing REST API BDD tests. Test implementation is almost the same as in the use of Rest-assured only, with a small allowance of the need to use the SerenityRest object as a „prefix”.
A great benefit of Serenity are beautiful reports which contain complete request/response information, what makes test analysis much easier.
Sources
Poznaj mageek of j‑labs i daj się zadziwić, jak może wyglądać praca z j‑People!
Skontaktuj się z nami


